Water treatment Chemicals

- Algaecides
- Antifoams
- Coagulants
- Corrosion inhibitors
- Disinfectants
- Chlorine (dose 2-10 mg/L)
- Chlorine dioxide
- Ozone
- Hypochlorite
- Flocculants
- Neutralizing agents
- Oxidants
- pH conditioners
- Resin cleaners
- Scale inhibitors
RO System

RO Membrane

Membrane Module

Reverse Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis / RO is a technology used to remove dissolved solids and impurities from water using a semi-permeable RO membrane which allows the passage of water but leaves the majority of dissolved solids and other contaminants behind. The RO membranes require water to be under high pressure (greater than osmotic pressure) to do this. The water that passes through the RO membrane is referred to as the "permeate" and the dissolved salts that are rejected by the RO membrane is referred to as the "concentrate". A properly run RO system can remove up to 99.5% of incoming dissolved salts and impurities.
Reverse Osmosis is capable of removing up to 99%+ of the dissolved salts (ions), particles, colloids, organics, bacteria and pyrogens from the feed water (although an RO system should not be relied upon to remove 100% of bacteria and viruses). An RO membrane rejects contaminants based on their size and charge. Any contaminant that has a molecular weight greater than 200 is likely rejected by a properly running RO system Likewise, the greater the ionic charge of the contaminant, the more likely it will be unable to pass through the RO membrane. Because an RO system does not remove gases, the permeate water can have a slightly lower than normal pH level depending on CO2 levels in the feed water as the CO2 is converted to carbonic acid.
A semi-permeable membrane is a membrane that will allow some atoms or molecules to pass but not others. A simple example is a screen door. It allows air molecules to pass through but not pests or anything larger than the holes in the screen door. Another example is Gore-tex clothing fabric that contains an extremely thin plastic film into which billions of small pores have been cut. The pores are big enough to let water vapor through, but small enough to prevent liquid water from passing.
How does Reverse Osmosis work?
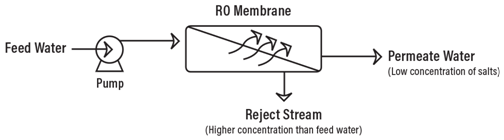
Reverse Osmosis works by using a high pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semi-permeable RO membrane, leaving almost all (around 95% to 99%) of dissolved salts behind in the reject stream. The amount of pressure required depends on the salt concentration of the feed water. The more concentrated the feed water, the more pressure is required to overcome the osmotic pressure. The desalinated water that is demineralized or deionized, is called permeate (or product) water. The water stream that carries the concentrated contaminants that did not pass through the RO membrane is called the reject (or concentrate) stream.

Filters (Sand, Activated carbon, Iron Removal & Water Softner Systems )
The Activated carbon Filters are designed to remove free chlorine, organic matter, odour and Colour present in the raw water and waste water. Due to its high degree of micro porosity, activated carbons provide a huge surface area.Activated carbon filter operates through adsorption. Adsorption is directly related to the surface area of the media. This great surface area furnishes a huge adsorption area for organic as well as chlorine molecules to attach themselves.

Filter media
- The sand must pass through a 12mm (1/2”) sieve. Anything larger than this can be discarded.
- Store the material that is captured by the 6mm (1/4”) sieve. This is used for the drainage gravel layer at the bottom of the filter.
- Store the material that is captured by the 1mm (0.04”) sieve. This will be used for the separating gravel layer just on top of the drainage gravel layer.
- Store the material that is captured by the 0.7mm (0.03”) sieve. Part of this material will be used to make the concrete filter box (if constructing a concrete filter). The rest will be further Shifted to make the sand filter media.

Ultrafiltration
Ultrafiltration is applied in cross-flow or dead-end mode and separation in ultrafiltration undergoes concentration polarisation. Ultrafiltration systems eliminate the need for clarifiers and multimedia filters for waste streams to meet critical discharge criteria or to be further processed by wastewater recovery systems for water recovery. Efficient ultrafiltration systems utilise membranes which can be submerged, back-flushable, air scoured or spiral wound UF/MF membranes that offer superior performance for the clarification of wastewater and process water. Augatech offers a range of industrial scale water filtration technologies depending on the chemical and physical components of the water supply to be treated.
Electrical panels

The distribution of power to the various circuits are protected from over-current by the use of circuit breakers or fuses. Once you open the door to the panel you can access all the circuit breakers or fuses. Usually one of these panels feeds all the circuits in the home but there may be a situation where there is another "sub-panel" serving a dedicated area like a new kitchen.
EFFLUENT TREATMENT PLANT

CETP

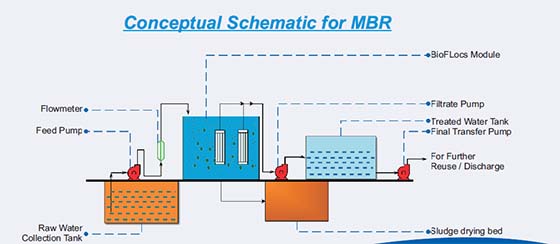
MBR
Membrane Bio-Reactor (MBR)
In coventional biological treatment process, the bioreactor and gravity clarifier are two separate units limiting the MLSS handled by the process. This limitation leads to higher foot print of the plant and higher sludge volume. Membrane Bio Reactor (MBR) based platform decouples reaction and clarification, making operation at higher MLSS possible. Also as majority of bacterial mass is in suspension, the efficiency is also better than its contemporary. Thus MBR based System is a very powerful tool to treat wastewater in most stringent of conditions. In this process, sewage treatment operates at a very high MLSS (Mixed Liquor suspended Solid) compared to other conventional Activated Sludge process leading to significant benefits in space, time and performance.
Advantages of MBR :
- Compact treatment plants.
- Zero start-up time.
- Good outlet water quality.
- Automated operation.
- Negligible use of chemicals.
- Option to utilize the concentrate for Bio gas production.
- On demand treatment.
Applications of MBR :
- Sewage Treatment.
- Effluent Treatment.
- Drinking water treatment plants.
- Compact sewage treatment plants.
- Food industries.

Sequencing batch reactor (SBR)

A Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR) is a “process” and not a “product”. Each SBR wastewater treatment system is designed to meet the specific requirements of each project. It is built in accordance with design criteria supplied in the form of a technical specification or as required to meet varying influent and effluent characteristics and flows. SBR is an extremely efficient and well-proven biological treatment process which is used to biodegrade organic matter and can also offer significant nitrogen reductions from the wastewater to deliver a treated wastewater that exhibits a very high level of BOD, COD and Nitrogen reduction along with high levels of reduction in suspended solids. This treatment process is ideally suited to high treatment volumes requiring Class A effluent quality in a compact arrangement. BOD and COD are used to measure water quality, with BOD used to determine how fast biological organisms use up oxygen in a body of water while COD measures the amount of organic compounds in water.
Minimal Footprint
A SBR system has a much smaller footprint than the traditional method of attempting to hardness a number of submerged aerated filters (SAF) or other fixed film activated sludge systems together.
DM PLANT
Demineralization is the process of removing mineral from the water . De minerialized Water is also known as Deionized Water, Water that has had its mineral ions removed. Mineral ions such as cations of sodium, calcium, iron, copper, etc and anions such as chloride, sulphate, nitrate, etc are common ions present in Water.
Ion Exchange Resins
There are two basic types of resin - cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins. Cation exchange resins will release Hydrogen (H+) ions or other positively charged ions in exchange for impurity cations present in the Water. Anion exchange resins will release hydroxyl (OH-) ions or other negatively charged ions in exchange for impurity anions present in the Water. The application of ion-exchange to Water treatment and purification. There are three ways in which ion-exchange technology can be used in Water treatment and purification: first, cation-exchange resins alone can be employed to soften Water by base exchange; secondly, anion-exchange resins alone can be used for organic scavenging or nitrate removal; and thirdly, combinations of cation-exchange and anion-exchange resins can be used to remove virtually all the ionic impurities present in the feed Water, a process known as deionization. Water deionizers purification process results in Water of exceptionally high quality


Advantages :
- Variety of cost effective standard models.
- Improved aesthetics and rugged design.
- User friendly, low maintenance and easy to install.
- Simpler distribution and collection systems.
- Quick availability.
- Pre dispatch assembly check.
- Rust free.
- Less power consumption.
- Durable.
- Economical.
- The multiport valves are top mounted as well as side mounted with the necessary high pressure rating PVC piping.
- Single valve operation as compared to the six valves in conventional filters.
- Each operating step is clearly marked on the valve, thereby eliminating chances of error in the operating sequence.
- Single valve assembly, with its simplified frontal Piping, simpler distribution collecting systems is Very easy to install.
- High shelf life.
The following ions are widely found in raw Waters:
Cations :
- Calcium (Ca2+)
- Magnesium (Mg2+)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Potassium (K+)
Anions :
- Chloride ( Cl-)
- Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
- Nitrate (NO3-)
- Carbonate (CO32-)
2017 Designed & Maintained By Webomindapps
